Partner Facilities
Momentum One Zero focuses on driving global change by harnessing digital technology and data innovation. Their R&D strategy is centred on solving critical global challenges through multidisciplinary research in fields like cybersecurity, health, and agri-food, leveraging Queen's University expertise. By aligning with economic priorities, Momentum One Zero fosters partnerships and builds capacity to fuel sustainable growth. Their mission includes expanding digital innovation to improve sectors worldwide and addressing the data revolution to meet complex business and societal needs.
Answering a global need
As the world goes digital, we must find new ways to process and protect the huge volumes of data we are creating. With an estimated 2.3 billion people across the globe relying on devices and the cloud to communicate, manage finances, access healthcare and even interact with household devices, new technological challenges are emerging every day.
At Momentum One Zero, our experts are on a mission to make this changing digital space both safer and faster. We are always one step ahead and are developing cutting-edge solutions to communicate even faster but in a safe and secure way. We are problem solvers, using our unique insight to come up with innovative ways to collect and store the huge volumes of data being created and shared across the globe every single day.
At the unique research and innovation centre academics, engineers and business development staff are working closely with world-leading companies and entrepreneurs, taking a business focused and entrepreneurial approach to tackling three areas of the global challenge. Discover more, visit www.momentumonezero.com
Three "Grand Challenges" direct research in the IGFS, i.e., farms of the future; global food integrity; and food, nutrition & health. It's purpose is to enhance agricultural outputs without compromising ecological stability, and employ new technologies to empower farmers and vets to monitor and control disease, check soil health, etc., and manufacturers to take advantage of digital technologies and automation for food-fingerprinting, detect contamination, sustain quality, efficient production, etc. The IGFS has extensive research facilities with a base in the School of Biological Sciences - a recent £40m investment.
The Institute for Global Food Security (IGFS) is one of four Global Research Institutes at Queen's University Belfast, established to address key, international challenges - in this case, the future of the world's food systems.
More than 70 Principal Investigators (PIs) and their teams at IGFS, which grew out of the School of Biological Sciences, aim to address challenges facing each link of the food chain
- IGFS is multi-disciplinary; researchers collaborate across schools and faculties (eg. Chemistry, Pharmacy, Geography, Medicine, Biological Sciences) and specialisms including sustainability, nutrition, agriculture and food safety.
- They routinely partner with industry for a solutions-led approach.
- Researchers help detect fraud and develop 'fingerprinting'; they study soil, crops, water and marine life, animal feed and animal welfare to promote higher standards.
- They trace chemicals (both natural and manmade) and investigate the nutritional value of foods and the psychology of consumer choices.
Discover more, visit IGFS
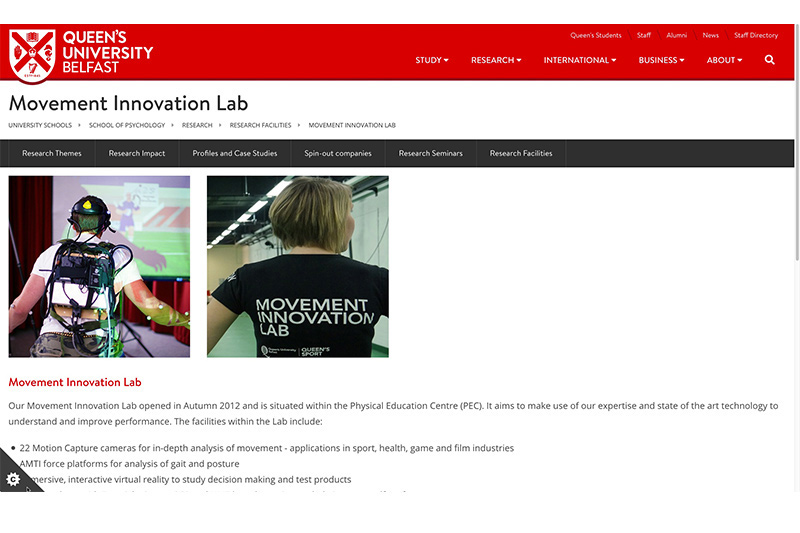
In the laboratory researchers investigate how people move and how sensory data from real or virtual environments influences movement. An experimental space with a tracking volume of 100m³ with sophisticated technology to monitor and analyse movement. The ideal facility to explore virtual and augmented reality, and how people interact with autonomous manufacturing systems and digital technologies.
Our Movement Innovation Lab opened in Autumn 2012 and is situated within the Physical Education Centre (PEC). It aims to make use of our expertise and state of the art technology to understand and improve performance.
The facilities within the Lab include:
- 22 Motion Capture cameras for in-depth analysis of movement - applications in sport, health, game and film industries.
- AMTI force platforms for analysis of gait and posture.
- Immersive, interactive virtual reality to study decision making and test products.
- Golf simulator with Foresight Sports GC2 and HMT launch monitor, to help improve golf performance.
Discover more, visit MIL

The centre is a technology hub for the research and development of advanced engineering and advanced materials technologies across a range of industrial sectors. A particular area of expertise is in composites, e.g., joining techniques, inspection and repair, tooling, recycling, advanced manufacturing techniques, etc.
NIACE brings together engineering companies and knowledge providers to work on projects developing technical expertise and helping support innovation and product development.
Our expertise and capability supports multiple sectors including Aerospace, Automotive, Construction, Marine, Renewables and Space.
We offer knowledge and skills together with access to likeminded businesses in different aspects of engineering and manufacturing through workshops and introductions to new technologies. We provide an opportunity to reduce development times, share project responsibility, have the potential to access funding and provide access to equipment for manufacturing and testing not currently available to the company.
Organisations across the globe can be members, working on joint projects and de-risking of research and development activities.
Discover more, visit NIACE
The centre links academic research and commercial production in a broad range of sectors, e.g., aerospace, industrial equipment, energy, consumer products, agri-food, etc. Though a multi-million pound investment the centre has new advanced manufacturing equipment and provides researchers with a versatile manufacturing technology factory to develop, verify and validate digital manufacturing technologies.
Operating for over 40 years the Technology Centre specialises in design, knowledge engineering and manufacturing. It bridges the gap between academic research and commercial production to meet industries needs and offer advanced solutions for customers in various sectors, such as aerospace, industrial equipment, energy, consumer products, manufacturing and packaging. As a leading commercial service provider and one of Queen's University Belfast's primary links with industry, working with companies has led the NITC to build a strong international reputation, helping raise the local sector's value proposition and competitiveness.
- Facilitate the application of technology for social and economic benefit through collaboration between education and industry.
- Provide access to leading-edge technology and processes.
- Accelerate the positive and effective resolution of specific challenges identified by industry.
Discover more, visit NITC
The centre is a channel from academic research to advanced manufacturing technologies for industries that use polymers. The team conducts research into rotational moulding, polymer extrusion, injection moulding, blow moulding and thermoforming, and explores new polymeric materials, products and processes.
Research in various aspects of polymers, including processing, has been carried out in the School of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering at Queen’s for over 25 years. During this time substantial investment has been made in establishing and maintaining state of the art processing and analytical facilities.
Building on the long established processing expertise at QUB in rotational moulding and polymer extrusion and extending into injection moulding, blow moulding and thermoforming, the Polymer Processing Research Centre (PPRC) was established in 1996 to conduct and support leading edge, industrially exploitable, fundamental and applied R&D to demonstrably improve industrial competitiveness. In 2002 there followed the establishment of the Medical Polymers Research Institute (MPRI) forum for collaborative work in the field of new polymeric materials, products and processes for the medical devices and drug delivery industries.
Discover more, visit PPRC

The centre has a cleanroom facility with sophisticated semiconductor process equipment and class 100 and class 10 work stations. With these facilities the team research and develop micro-fabrication technology and build micro electro mechanical systems (MEMS) for sensor applications in biomedical, environmental, and industrial applications.
Queen's Advanced Micro-Engineering Centre (QAMEC) is a centre of excellence for research and development employing silicon MEMS technology1, FSS technology2 and novel device structures. In collaboration with the Centre for Wireless Innovation (CWI) Group, QAMEC has established itself in the design and fabrication of FSS components for the European Space Agency. Whilst primarily a MEMS facility, the facility offers support through technology transfer, training and collaborative enterprise to industry in new growth areas.
QAMEC's core equipment set can accommodate silicon processing on various substrates, 50mm, 100mm diameter substrates and above, as well as offering the versatility of handling non-standard substrates such as Quartz, Sapphire and Germanium. For thin film work there is a wide range of PVD systems3 including dc and rf magnetron sputtering and CVD4 of layers such as silicon dioxide and silicon nitride. The centres additive manufacturing capability has recently been enhanced with the introduction of a Photonic Professional GT 3D polymer printing system from Nanoscribe, capable of 3D printing on a nano-scale. The Centre is set up as a versatile research laboratory rather than a dedicated IC production facility. This enables it to respond to an increasingly wide range of industrial needs.
[1] Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) are miniaturised mechanical and electro-mechanical elements made by micro-fabrication techniques, which can vary in size from below one micron to several millimetres.
[2] Frequency-selective surfaces (FSS) are any thin, repetitive surface designed to reflect, transmit or absorb electromagnetic fields based on the frequency.
[3] Physical vapour deposition (PVD), vacuum deposition methods used to produce thin films and coatings.
[4] Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD), deposition methods to produce dielectric films (Includes Plasma Enhanced PECVD and Low Pressure LPCVD)
Discover more, visit QAMEC